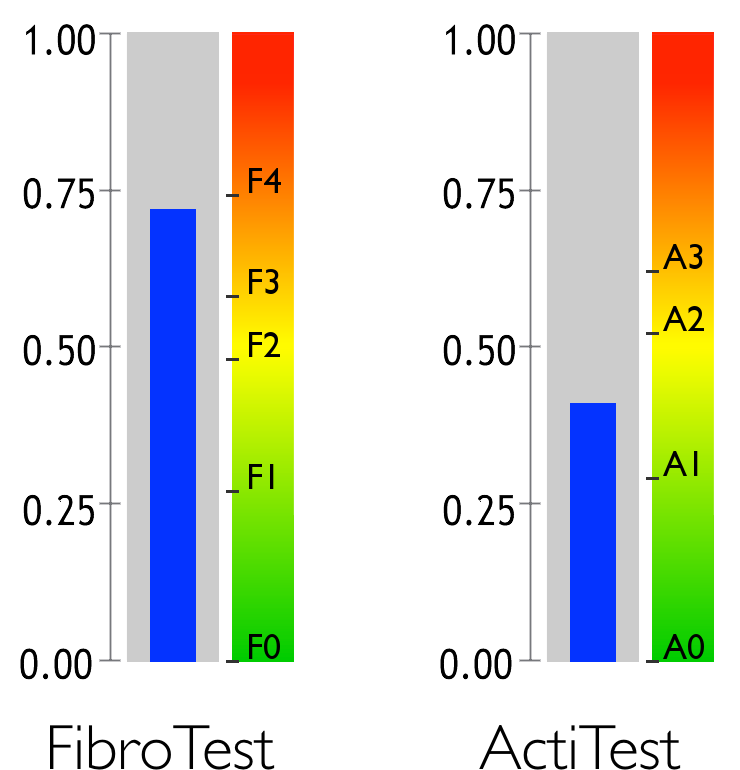
Fibrosis and activity are the two main causes of liver disease.
Fibrosis is a medical condition caused by the reaction of a diseased liver. Hepatic fibrosis is typically compared to a form of scar tissue that progresses throughout the liver. The most serious stage of fibrosis is known as cirrhosis.
Activity is liver inflammation caused by disease. It is often compared to a burn.
FibroTest is recommended by WHO 1 , the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) 2 , the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) 3 and the Asia-Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) 4 for evaluating hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C patients.
FibroTest is recommended EASL-ALEH 3 , APASL 4 and WHO 5 for diagnosing fibrosis in carriers of chronic hepatitis B virus.
FibroTest is recommended by the EASL-ALEH 3 for co-infected HIV carriers.
FibroTest is also used to provide access to new-generation non-interferon treatment for hepatitis C.
FibroTest is approved 6 and recommended by the European Associations for the Study of the Liver (EASL), Diabetes (EASD) and Obesity (EASO) 7 for the purpose of evaluating fibrosis in patients suffering from metabolic conditions (NAFLD) and by EASL when evaluating patients who consume excess alcohol 7 8 .
FibroTest is protected by an international patent and is founded on hundreds of scientific publications.
FibroTest is a non-invasive test that is applicable to the largest number of patients (98%) as well as being the most reliable 9 .
FibroTest offers the best performance of any test, at all stages of fibrosis: from a healthy liver to cirrhosis 10 .
Out of all non-invasive tests, FibroTest is the least sensitive to known risk factors for false positives and false negatives, such as necroinflammatory activity and steatosis, and it is not operator-dependent 11 .
The cost of FibroTest may be met, in whole or in part, by health insurance organizations (both public and private) depending on the country.
| FibroTest | Transient Elastography | APRI | FIB-4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applicability | ||||
| Performance from F0 to F3 | ||||
| Performance for F4 | ||||
| False positive due to inflammation | ||||
| Cost | ||||
| Prognostic |
Comparison table 10 showing different methods for testing for fibrosis
FibroTest combines five standard biomarkers
ActiTest adds a direct marker for inflammatory activity:
These markers are weighted depending on the patient's age and sex.
Tests may take place in any local medical test laboratory that is compliant with BioPredictive's technical recommendations.
There is no need to fast to have FibroTest-ActiTest
Where to do the test Technical RecommendationsYou can also access the scientific literature about FibroTest-ActiTest, and the latest news on non-invasive testing for the liver.
FibroTest and ActiTest are also included in NASH-FibroTest™, which offers a more complete picture of the condition of the liver.
Find out more