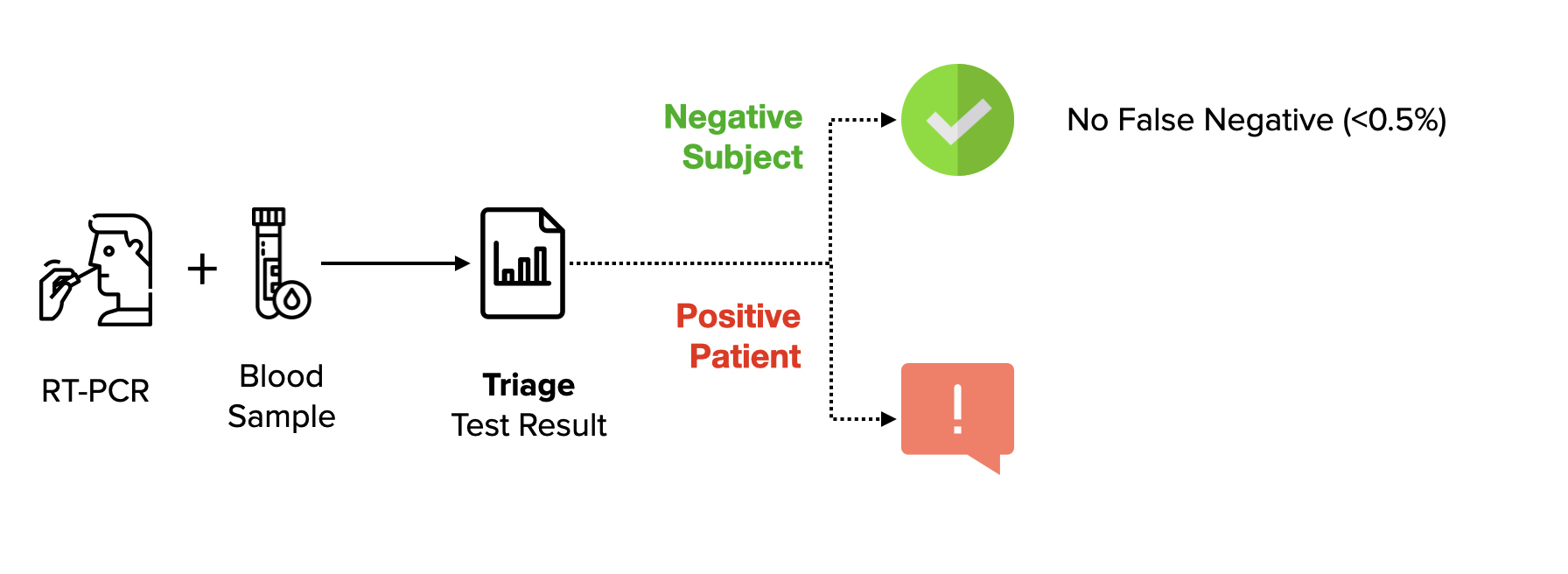
Cov-Secure is the first blood-based Covid-19 diagnostic test
A simple blood sample offers an unprecedent negative predictive value.
Using this test, negative subjects know they are Covid-free.
Using this test, negative subjects know they are Covid-free.
There are two ways to use the Cov-Secure test:
either at the same time as the RT-PCR, to lower the false-negative rate of the diagnostic
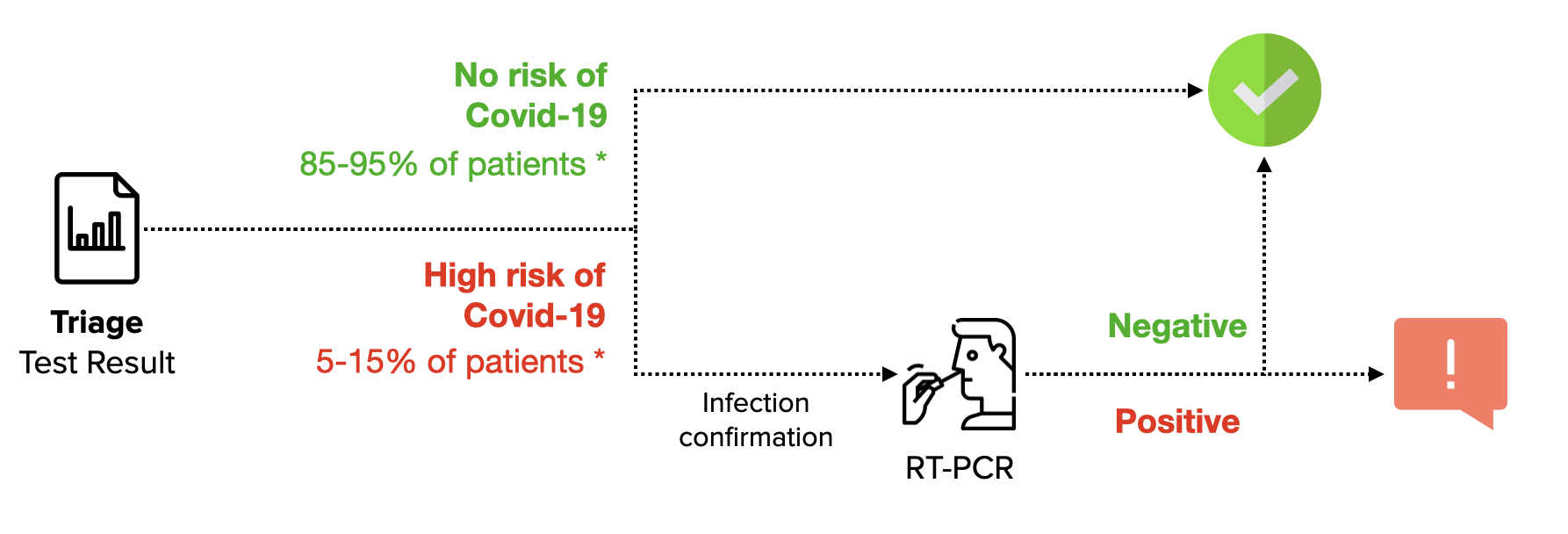
or as a first-line test for Covid-Free zones (negative subjects will likely not have the Covid-19)
Unlike other Covid-19 diagnostic tests (including RT-PCR, antigenic and RT-Lamp), Cov-Secure is blood based. There is no variability in the results due to the sample collection.
Indeed a major part of the false-negative results of the RT-PCR and antigenic tests is due to the naso-pharyngeal sample collection.
Using the Cov-Secure test, based on a standard blood-draw, there is no such variability, leading to a much safer test result.
either as a confirmation of RT-PCR, reducing false-negative
or as a first-line test, reducing RT-PCR by 80%
Comparison table 1 showing different methods for testing for fibrosis
Cov-Secure combines two standard biomarkers
These markers are weighted depending on the patient's age and sex.
Tests may take place in any local medical test laboratory that is compliant with BioPredictive's technical recommendations.
There is no need to fast to have Cov-Secure done
Where to do the test Technical Recommendations